AboutUniversal Habitat Sustainable Development

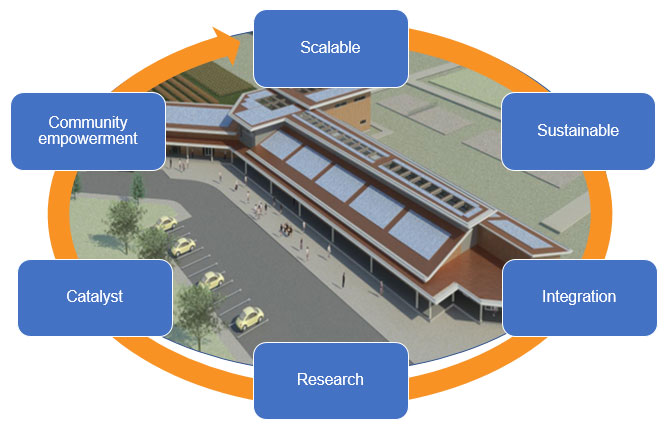
An integrated infrastructure development platform. Habitat in this instance refers to the built environment, apropos sustainable community buildings that meet their constituent needs through provision of integrated renewable energy technologies within the fabric of the building.
A scalable integrated green solution which can be deployed collaboratively that emphasises the need to incorporate not just equipment into resilient buildings but also offers research, training and education programmes.
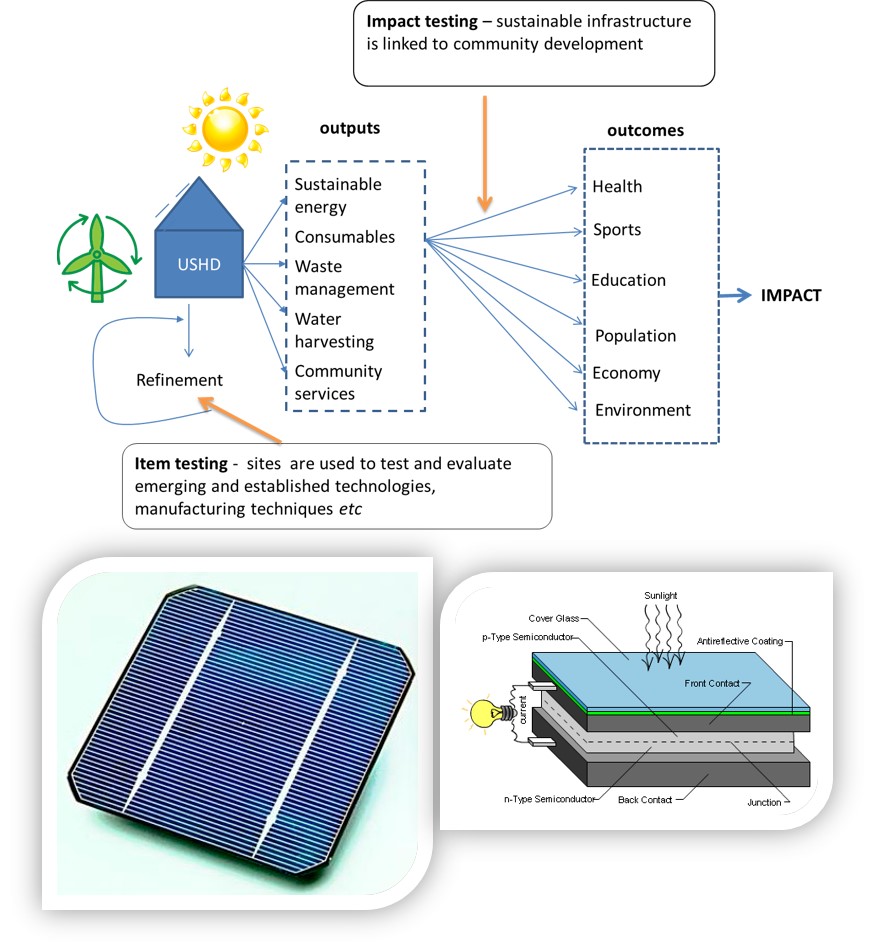
Hybrid renewable technology solutions
Photovoltaic panels
PV cells are made from layers of semi-conducting material, usually silicon. When light shines on the cell it creates an electric field across the layers. The stronger the sunshine, the more electricity is produced. Groups of cells are mounted together in panels or modules that can be mounted on roofs.
- Cheap to install
- Reduced energy bills
- Get paid for the electricity you generate:
- Cut your carbon footprint: solar electricity is green, renewables energy and doesn't release any harmful carbon dioxide] or other pollutants. A typical home solar PV system could save over a tonne of carbon dioxide per year – that's more than 30 tonnes over its lifetime.
Solar water heating systems use free heat from the sun to warm domestic hot water. A conventional boiler or immersion heater can be used to make the water hotter, or to provide hot water when solar energy is unavailable.
- Cheap to install
- Reduced energy bills
- Cut your carbon footprint: solar hot water is a green, renewable heating system and can reduce your carbon dioxide emissions.
